We report VEP studies which delineate interactions between chromatic and luminance contrast signals. We examined responses to sinusoidal luminance gratings undergoing 4 Hz square wave contrast-reversal, upon which standing gratings with various admixtures of luminance and chromatic contrast were alternately superimposed and withdrawn. The presence of the standing grating induced a VEP component at the fundamental frequency of the contrast-reversal grating. This VEP component appeared without any appreciable lag, and did not vary in amplitude over the 4 sec during which the standing grating was present. The observed fundamental response differed from the fundamental component that would be expected from the known interaction between the luminance component of the standing grating with the modulated grating (Bodis-Wollner, Hendley, & Kulikowski 1972; Bobak, Bodis-Wollner, & Marx 1988), in three ways: (i) The fundamental response was not nulled for standing gratings that were isoluminant or near-isoluminant. (ii) The chromatic dependence of the fundamental response implied an S-cone input to the interaction. (iii) No single mechanism (driven by a linear combination of cone signals) could account quantitatively for the size of this response, particularly when the standing grating strongly modulated two cones in phase.

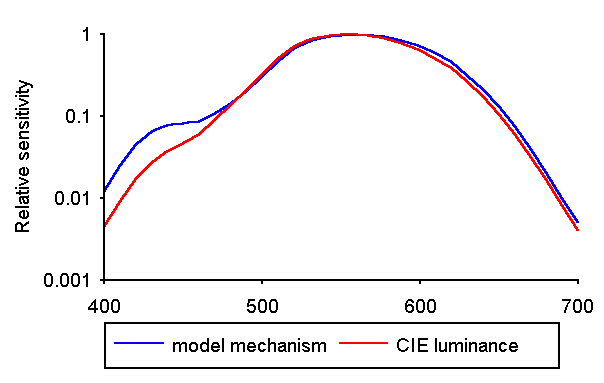
We show that chromatic signals modulate the responses to luminance contrast. This figure indicates the derived spectral sensitivities of mechanism which drives the interaction with luminance contrast. The mechanism has inputs from short wavelength cones, which distinguishes it from the standard CIE photopic luminance sensitivity function.